What is the role of cooling towers?
Firstly, a cooling tower is used to cool the water :
- Either alone, or in addition to chillers for HVAC application: office buildings, shopping malls, hospitals, university campus, data centres, etc.
- All industrial process requiring its production cycle to be cooled : sugar mills, distilleries, petrochemicals, agri-food industry, Iron & steel production, R&D, power plant generation, etc.
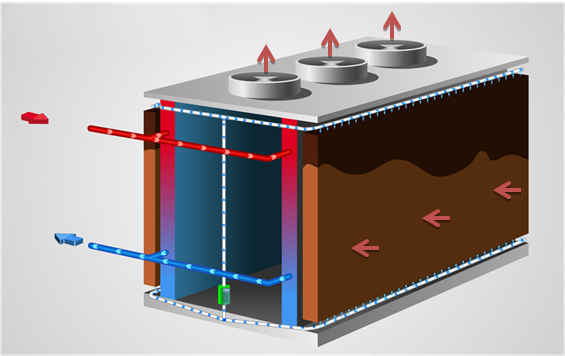
The cooling operates through an air/water exchange surface (packing or infill), this air is directly in contact with the water and allows, by evaporation of a few quantities, to reduce its temperature. In this way, it is then possible to cold water to a lower temperature than dry ambient one.
What are the benefits of cooling towers?
Cooling systems optimize performance by:
- Controlling the electric consumption,
- Lowering its water consumption,
- Limiting maintenance downtime for ever-increasing equipment availability and controlled operating costs.
What kind of cooling tower for what kind of application ?
The choice of a cooling tower is subjected to a personalized study to answer each specific requirement:
- application type, industrial or HVAC,
- water quality to be cooled (preponderant choice of the infill),
- thermal power to be rejected and / or water flow to be cooled,
- required cold water temperature,
- dedicated area for its installation and the environment according to sound levels or visual requirements (plume abatement).
Open, closed or hybrid cooling tower ?
The cooling towers can be constituted by two types of cooling circuit: an open circuit or closed circuit. The type of cooling system is going to be decisive for the exact way in which heat transmission occurs.
Indeed, the efficiency of the processes is directly linked to the operating temperature of the water circuits.
Therefore, evaporative cooling remains the most economical process. Cold water temperatures are reach, lower than the ambient temperature.
Open circuit cooling tower:
An open cooling towers has no physical separation between user circuit (process) and cooling tower circuit. The water to be cooled goes directly inside the cooling tower, distributed at the top of the equipment homogeneously over the hole surface of the infill. Directly in contact with the water, the air, by evaporation of a few quantities, reduces its temperature. A mechanical fan, induced drat or forced draft, allows the air to go against the water current. The cold water is then collected in the basin to go back to user process.
Main benefits :
- The equipment allows reaching the lower water temperatures possible.
- Compact equipment.
Closed circuit cooling tower:
A closed cooling tower has a physical separation between the user circuit (process) and the cooling tower circuit. The water to be cooled goes through a plate heat exchanger coupled together with an open circuit cooling tower. In this way, both circuits are separated and thermal exchange operates on one hand through the plate heat exchanger for user circuit, and on the other hand through the infill with the same evaporative operation than inside an open cooling tower.
Main benefits:
- Process water is not in direct contact with cooling tower water.
- Water quality control and no bacteria’s development risk.
- Easy and safe maintenance as limited by water quantity inside the cooling tower.
- Low water treatment cost, linked with strict water volume of the cooling tower.
Hybrid open or hybrid closed circuit cooling tower:
A hybrid open or closed circuit is a cooling tower completed by a dry plume abatement coil. Settled at the top of the cooling tower, the plume coil allows reducing or even eliminate the plume. Plume at the outlet of a cooling tower could be wrongly associated to pollution, but it is only water vapour.
Hybrid cooling tower efficiency is ensured by a finned tube coil combined with a valve for adjusting the water spray on the exchange surface (infill) : JACIR patent.
Therefore, the combination of the air desaturation by air outlet warming up, and the reduction of the water spray on the packing, ensures the complete plume suppression. Beyond the plume suppression itself, this system can provide water savings up to 80 % and is an ultimate obstacle to the drifts
JACIR makes a point of ensuring the quality, the ease of use and operation of its cooling systems. For this, solutions exist, and must be optimized from the design stage.
- Maintenance access is facilitated, allowing sufficient access to act quickly and safely.
- Our equipment is designed to limit water and energy consumption, maintain performance over time, and allow regulation according to process demand, variations in external conditions and the working environment.
- Manufacturing quality is ensured in order to control maintenance expenses and allow our cooling towers to be programmed to prevent production hazards in the long term.
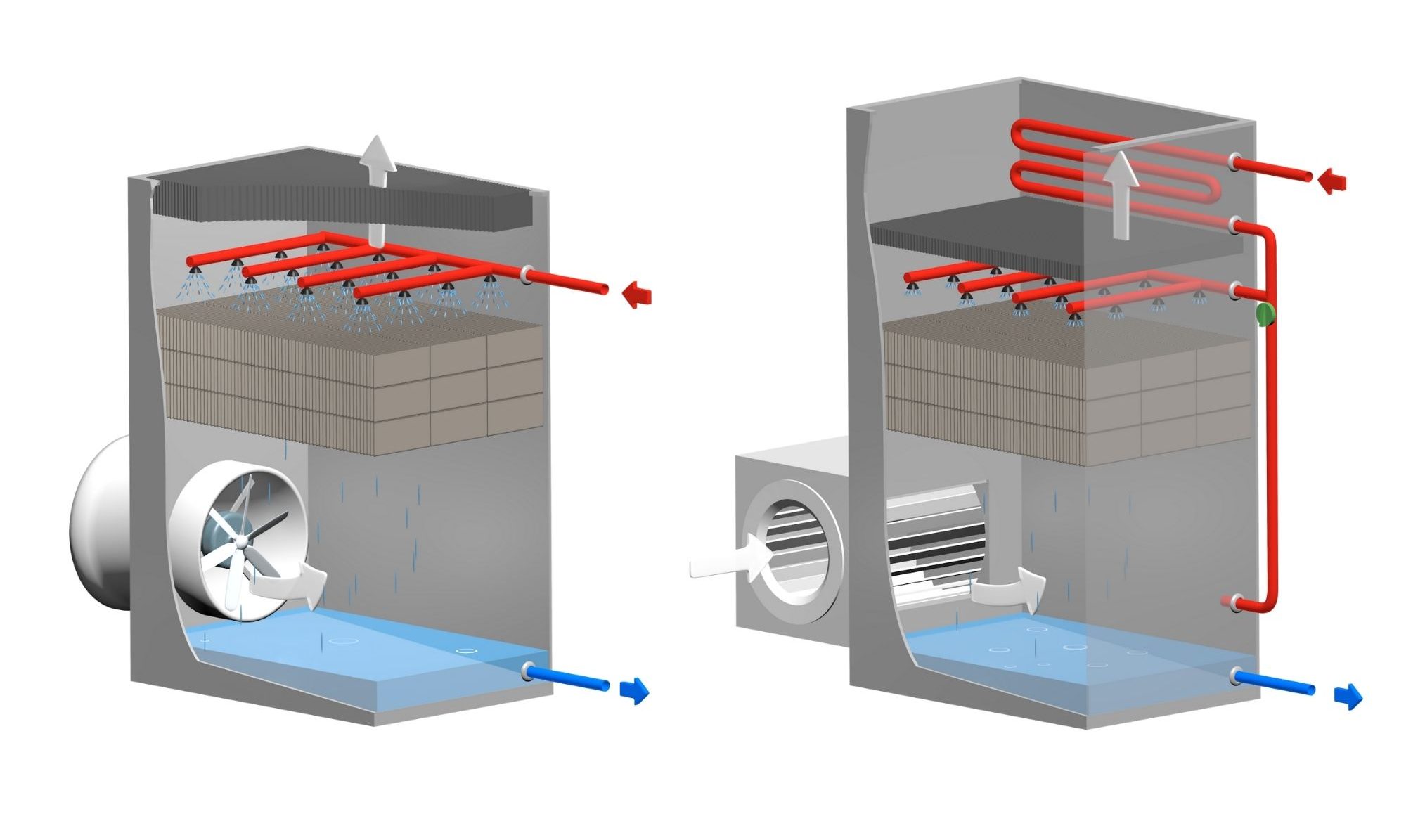
Open cooling towers
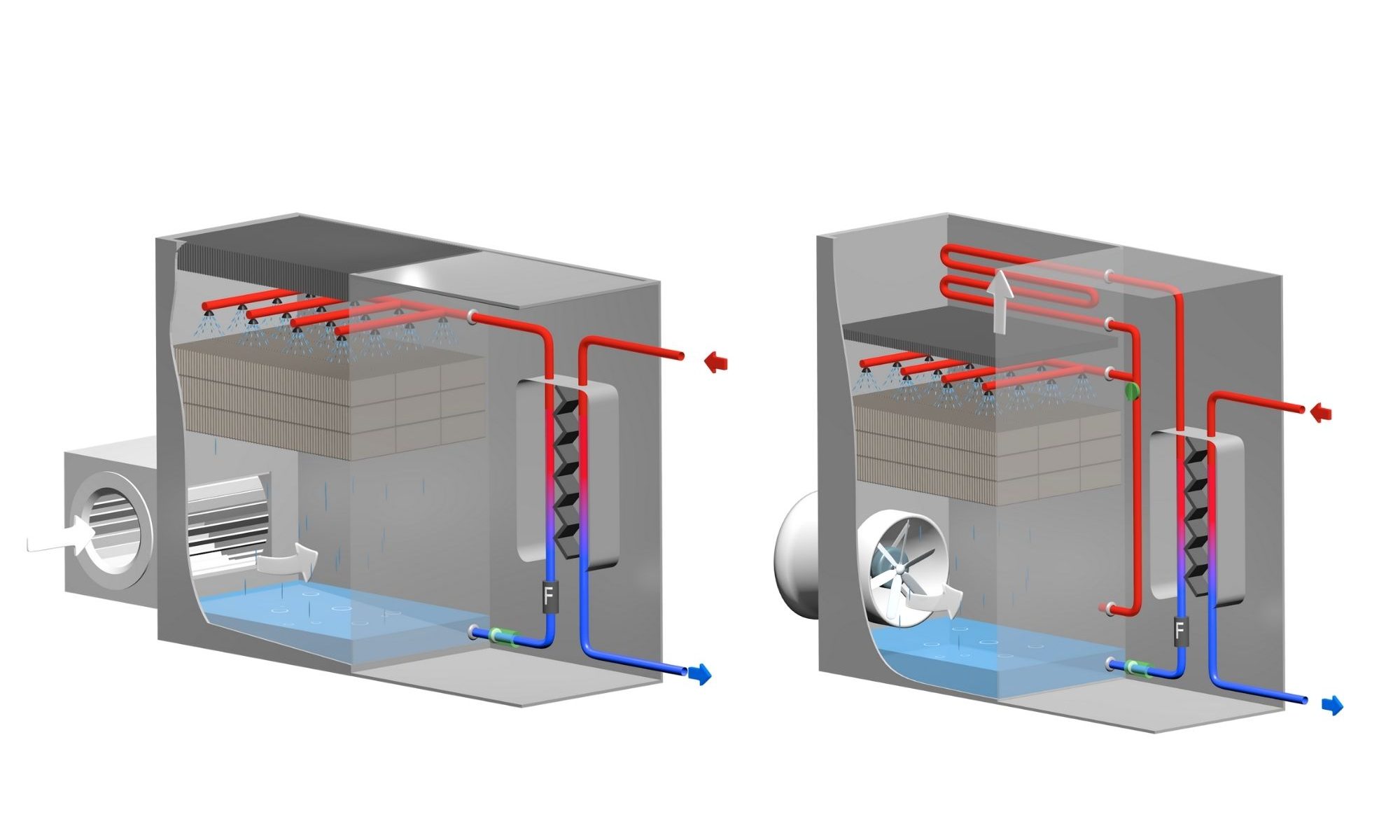
Closed cooling towers
Adiabatic cooler :
An adiabatic cooler is a combination of dry cooler with an adiabatic precooling section.
This precooling section lowers ambient air temperature by evaporating water which is passed over the cooling / humidifying pads, specially designed for this purpose.
Dry mode
The fluid is cooled inside to vertical coils by ambient air flow. The ambient air is drawn through the coils by fans mounted centrally on the top of the Cooler; the humidifying pads located in front of the coils are dry.
The fan speed is controlled by an inverter depending on heat load to maintain the fluid outlet temperature.
The warm air is then evacuated upwards.
Adiabatic mode
When cooling in dry mode is not effective and the ambient temperature reaches a predetermined set point, the water is going over the pads (media).
The ambient air is cooled by evaporation when passing through the pads : this precooled air then passes through the tube coils and cools the fluid.
The water which has not been evaporated on the pads is collected in a stainless steel tank and is then recycled by a sump.
The water saving is then significant and does not require water treatment, it is without risk of Legionella.
Main benefits :
- No drift
- Low water consumption thanks to sump recycling system
- Easy access (complete access inside the equipment for maintenance)
- No water treatment
Important parameters to be taken into account :
The choice of a cooling circuit type is preponderant : it depends on the exact way heat transfer is realised.
Cooling operation efficiency is directly linked to the operation water circuits temperatures.
Evaporative cooling remains the most affordable method in order to produce lower cold water temperatures than ambient one.
An efficient cooling tower will have to optimize returns by mastering energy consumption, reducing water consumption, restricting maintenance downtimes for always more operational equipment, with costs of operation under control.
Technical solutions are in place, and it is important to think ahead in equipment design :
To ease maintenance access, allowing sufficient space to take action quickly and safely.
To propose cooling towers specially designed to confine consumptions, to maintain the performance over the time, and to adapt a possible regulation according the process need, outside weather variation or working environment.
To ensure a manufactured quality in order to control maintenance costs, allowing a long term schedule in order to prevent production hazards.
What is the difference between a natural draft tower and a forced draft cooling tower?
The concrete hyperboloid type natural draft cooling tower (as seen in the nuclear industry) uses the “stack effect” to remove heat from the water to be cooled.
The hot water is distributed at the top of the tower, slowed down by the exchange surface, taking advantage of the action of the natural wind to be cooled by gravity.
Part of the water, by evaporating, causes its temperature to naturally drops.
Forced draft makes it possible to overcome the action of natural wind using a motorized fan unit for smaller metal or polyester units.
This mechanical forced extraction improves the performance and regularity of the air flow, without influence of weather conditions.
These motorized fan groups can be positioned at the bottom of the device (centrifugal ventilation) or at the top of the tower (helicoid ventilation).
The choice of the type of ventilation generally depends on the constraints of the installation: quantity of water to be cooled, low energy consumption, noise level, size, etc., and are used on all types of lathes, open or closed circuit.